How Long Does Alcohol Poisoning Last
Alcohol poisoning, also known as alcohol overdose or alcohol toxicity, is a potentially life-threatening condition caused by excessive alcohol consumption in a short period. It occurs when the body’s ability to process alcohol is overwhelmed, leading to a buildup of toxic levels of alcohol in the bloodstream. This can result in a range of serious consequences, from immediate physical and mental impairments to long-term health problems or even death.
Understanding how long alcohol poisoning lasts, recognizing the signs and symptoms, and knowing when to seek medical attention are crucial for preventing serious complications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of alcohol poisoning, exploring its timeline, effects, and treatment options.

How Long Does Alcohol Poisoning Last? A Detailed Look at Duration and Recovery
Alcohol poisoning, a consequence of excessive alcohol consumption, is a serious condition with potentially fatal outcomes. The duration for the effects of alcohol poisoning and the subsequent recovery timeline can vary greatly from person to person, influenced by several factors. Understanding the duration of this potentially life-threatening condition and the steps involved in recovery is crucial for both individuals who have experienced it and those who are concerned about alcohol abuse in their loved ones.
Factors Affecting Alcohol Poisoning Duration:
How Much Alcohol Consumed: The quantity of alcohol consumed is a primary factor in determining how long alcohol poisoning lasts. Higher amounts of alcohol take longer for the body to process and eliminate, resulting in a longer duration of intoxication and potentially more severe symptoms.
Individual Factors: Each person’s body processes alcohol differently. Factors like body weight, metabolism, age, and overall health can significantly influence how long it takes to recover from alcohol poisoning.
Food Consumption: Eating before or during alcohol consumption can slow down alcohol absorption, potentially reducing the severity and duration of alcohol poisoning.
Other Substances: Consuming alcohol mixed with other drugs can have unpredictable and dangerous effects, potentially prolonging the duration of alcohol poisoning and increasing the risk of complications.
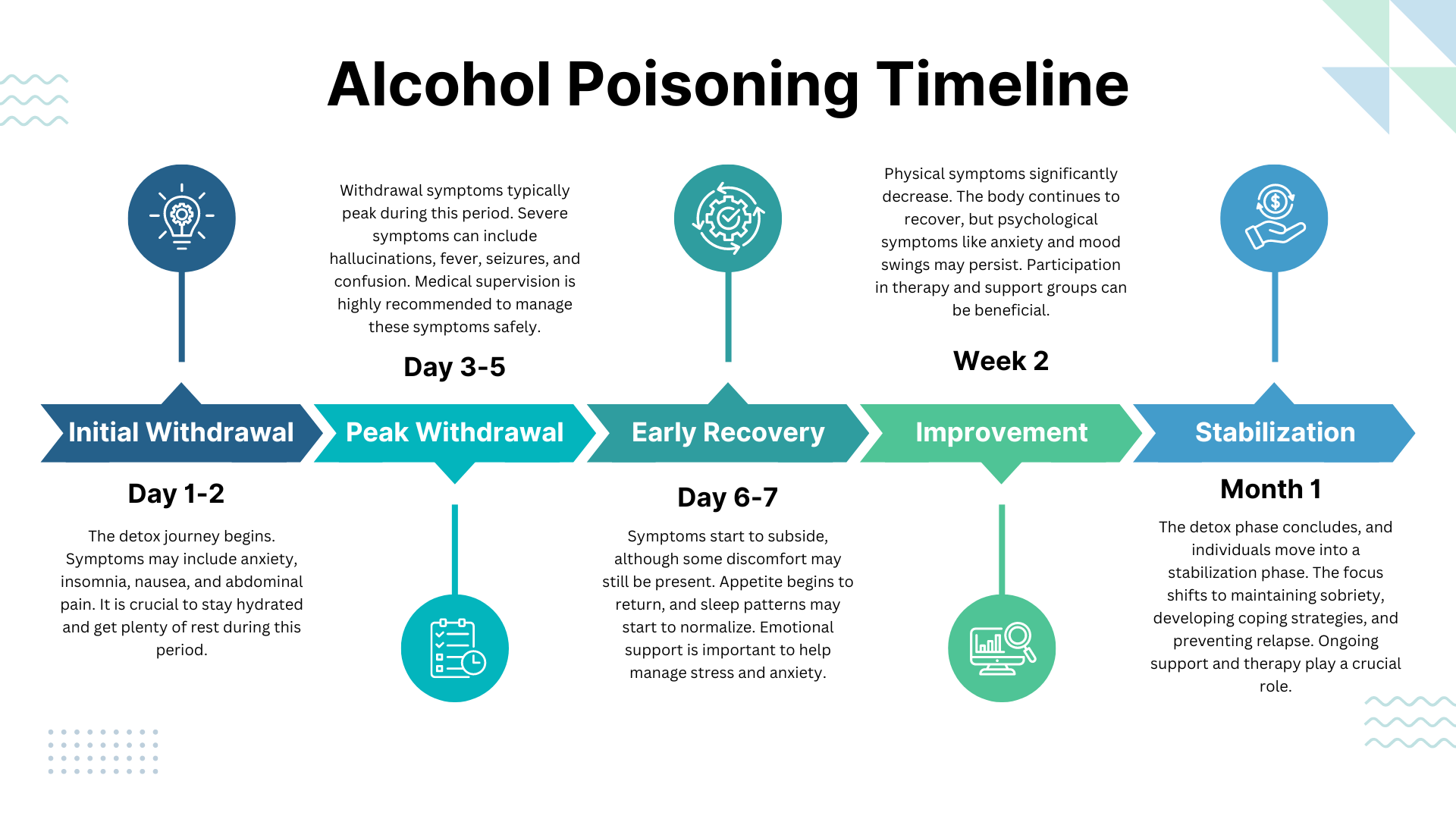
Alcohol Poisoning Timeline
The timeline of alcohol poisoning symptoms typically follows this pattern:
Initial Effects of Alcohol Poisoning (Minutes to Hours): As the blood alcohol concentration (BAC) rises, individuals may experience the initial effects of alcohol intoxication, such as impaired judgment, slurred speech, loss of coordination, and nausea.
Peak Intoxication (Hours): BAC levels reach their peak, and the risk of alcohol poisoning is highest. This is when severe symptoms, such as confusion, vomiting, seizures, irregular breathing, and loss of consciousness, severe dehydration may occur.
Hangover Phase (Hours to Days): As the body begins to metabolize the alcohol, individuals may experience a hangover, characterized by headache, fatigue, nausea, and dehydration. These symptoms can last for several hours or even days, depending on the amount of alcohol consumed and the individual’s overall health.
Recovery Phase (Days to Weeks): The body continues to eliminate alcohol and repair any damage caused by the poisoning. During this phase, individuals may experience lingering symptoms, such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and mood swings. In severe cases, long-term complications, such as brain damage or liver problems, may occur.
Alcohol Poisoning Symptoms: A Warning Sign
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of alcohol overdose is crucial for seeking timely medical attention. Some common symptoms include:
Mental Confusion: The person may be disoriented, confused, or unable to answer simple questions.
Vomiting: Persistent vomiting, especially if the person is unconscious or semi-conscious, can be a sign of severe alcohol poisoning.
Seizures: Seizures can occur due to the toxic effects of alcohol poisoning on the brain.
Slow or Irregular Breathing: Breathing may become shallow, slow, or irregular, which can be life-threatening.
Low Body Temperature (Hypothermia): Alcohol can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate temperature, leading to hypothermia, a dangerous drop in body temperature.
Loss of Consciousness: The person may pass out and be difficult to awaken.
Bluish or Pale Skin: This can indicate a lack of oxygen due to suppressed breathing.
Risk Factors for Alcohol Poisoning
Several factors can increase a person’s risk of experiencing alcohol poisoning symptoms:
Binge Drinking: Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol in a short period, also known as binge drinking, significantly increases the risk of alcohol overdose.
Age and Gender: Young people, particularly those under 21, are more vulnerable to alcohol poisoning due to their lower tolerance and inexperience with alcohol. Women are also at higher risk due to differences in body composition and metabolism compared to men.
Mixing Alcohol with Other Drugs: Combining alcohol with other drugs, such as prescription medications or illicit substances, can increase the risk of alcohol poisoning and other adverse effects.
Chronic Heavy Drinking: Individuals with a history of heavy drinking or alcohol addiction are more likely to experience alcohol poisoning.
How Much is Too Much Alcohol?
The amount of alcohol that can lead to alcohol poisoning effects varies depending on individual factors, but binge drinking is a common culprit. For women, binge drinking is defined as consuming four or more alcoholic drinks within two hours, while for men, it’s five or more drinks within the same timeframe.
However, it’s important to note that even lower amounts of alcohol can lead to alcohol overdose in some individuals, especially if they have a low tolerance or are taking medications that interact with alcohol.

Preventing Alcohol Poisoning: Tips for Responsible Drinking
Pace Yourself: Avoid drinking too much alcohol too quickly. Alternate alcoholic drinks with water or non-alcoholic beverages.
Eat Before and During Drinking: Food can help slow down the absorption of alcohol and reduce the risk of alcohol poisoning.
Know Your Limits: Be aware of your own tolerance and avoid exceeding it.
Avoid Mixing Alcohol with Other Drugs: Combining alcohol with other substances can be dangerous and increase the risk of adverse effects.
Don’t Drink and Drive: Never drink and drive or get into a car with someone who has been drinking.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you suspect someone is experiencing alcohol poisoning, seek immediate medical attention. Call 911 or your local emergency number right away. Do not wait for the person to “sleep it off,” as alcohol poisoning can quickly become life-threatening.
While waiting for medical assistance, try to keep the person awake and sitting upright. If they are unconscious, roll them onto their side to prevent them from choking on their vomit. Do not leave the person alone, and monitor their breathing and pulse closely.
Seeking Medical Attention: A Lifesaving Necessity
It’s crucial to emphasize that alcohol poisoning is a medical emergency. If you suspect someone is experiencing alcohol poisoning, immediate medical attention is imperative. Signs of alcohol poisoning include confusion, vomiting, seizures, slow or irregular breathing, cold or clammy skin, and loss of consciousness.
Prompt medical intervention can prevent life-threatening complications, such as choking on vomit, respiratory depression, and cardiac arrest. Medical professionals can provide supportive care, including intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration, oxygen therapy to support breathing, and medications to manage withdrawal symptoms.
Treatment for Alcohol Poisoning
Alcohol poisoning is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment. Treatment typically involves:
Supportive Care: Providing oxygen, fluids, and other supportive measures to stabilize the person’s condition.
Monitoring: Closely monitoring vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing.
Medications: In some cases, medications may be given to prevent seizures, control nausea, or manage other symptoms.
Gastric Lavage (Stomach Pumping): In severe cases, gastric lavage may be necessary to remove unabsorbed alcohol from the stomach.

Alcohol Addiction Treatment: A Path to Long-Term Recovery
While alcohol poisoning is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, it can also be a wake-up call for individuals struggling with alcohol abuse or alcohol use disorder. Seeking addiction treatment is crucial for those who have experienced alcohol poisoning, as it can help them address the underlying causes of their drinking behavior and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
Alcohol addiction treatment programs offer a comprehensive approach to recovery, combining various therapies and support services to address the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of addiction. These programs may include:
Detoxification: Medically supervised detox can help manage withdrawal symptoms and ensure a safe transition into recovery.
Individual and Group Therapy: Therapy sessionsprovide a safe space for individuals to explore the root causes of their addiction, develop healthy coping skills, and build a strong foundation for lasting sobriety.
Medication Management: Certain medications can be helpful in reducing cravings and managing withdrawal symptoms, making it easier for individuals to abstain from alcohol.
Support Groups: Support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), offer a sense of community and connection with others who understand the challenges of addiction and recovery.
By seeking professional help, individuals who have experienced alcohol poisoning can not only recover from the immediate effects of alcohol toxicity but also address the underlying causes of their alcohol abuse and achieve long-term sobriety. With the right treatment and support, recovery is possible, and individuals can regain control of their lives and build a healthier, happier future.
Conclusion
Alcohol poisoning is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. By understanding the timeline, symptoms, and risk factors, you can take steps to prevent it from happening and seek immediate medical attention if you suspect someone is experiencing alcohol poisoning.
Remember, responsible drinking is key to how to avoid alcohol poisoning. By pacing yourself, knowing your limits, and avoiding risky behaviors, you can enjoy alcohol safely and responsibly. If you or someone you know struggles with alcohol abuse or addiction, don’t hesitate to seek help. Recovery is possible, and many resources are available to support you on your journey to sobriety.
Seeking Treatment? We Can Help!
We work with PPO Out of Network Health Insurance Policies
If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges or substance abuse, reach out to Mountain Sky Recovery today. Our team of compassionate professionals is here to support your journey towards lasting well-being. Give us a call at 951-877-5868.
FAQs For What is the number one drug used by teens?
How long does it take to recover from alcohol poisoning?
Recovery from alcohol poisoning varies depending on several factors, including the amount of alcohol consumed, individual health, and how quickly medical treatment is received. Generally, the acute symptoms can last from several hours to a few days, while full recovery may take several days to weeks
What are the first signs of alcohol poisoning?
The first signs of alcohol poisoning include confusion, vomiting, seizures, slow or irregular breathing, bluish or pale skin, hypothermia, and unconsciousness. Immediate medical attention is crucial if these symptoms are observed.
Can eating food help prevent alcohol poisoning?
Yes, eating before or while drinking can slow down the absorption of alcohol into the bloodstream, potentially reducing the risk and severity of alcohol poisoning. However, it is not a guaranteed prevention method, especially if large amounts of alcohol are consumed quickly.
Is it safe to let someone with alcohol poisoning "sleep it off"?
No, it is not safe to let someone with alcohol poisoning sleep it off. Alcohol poisoning can worsen while the person is unconscious, leading to life-threatening complications such as choking, respiratory failure, or cardiac arrest. Always seek immediate medical attention.




